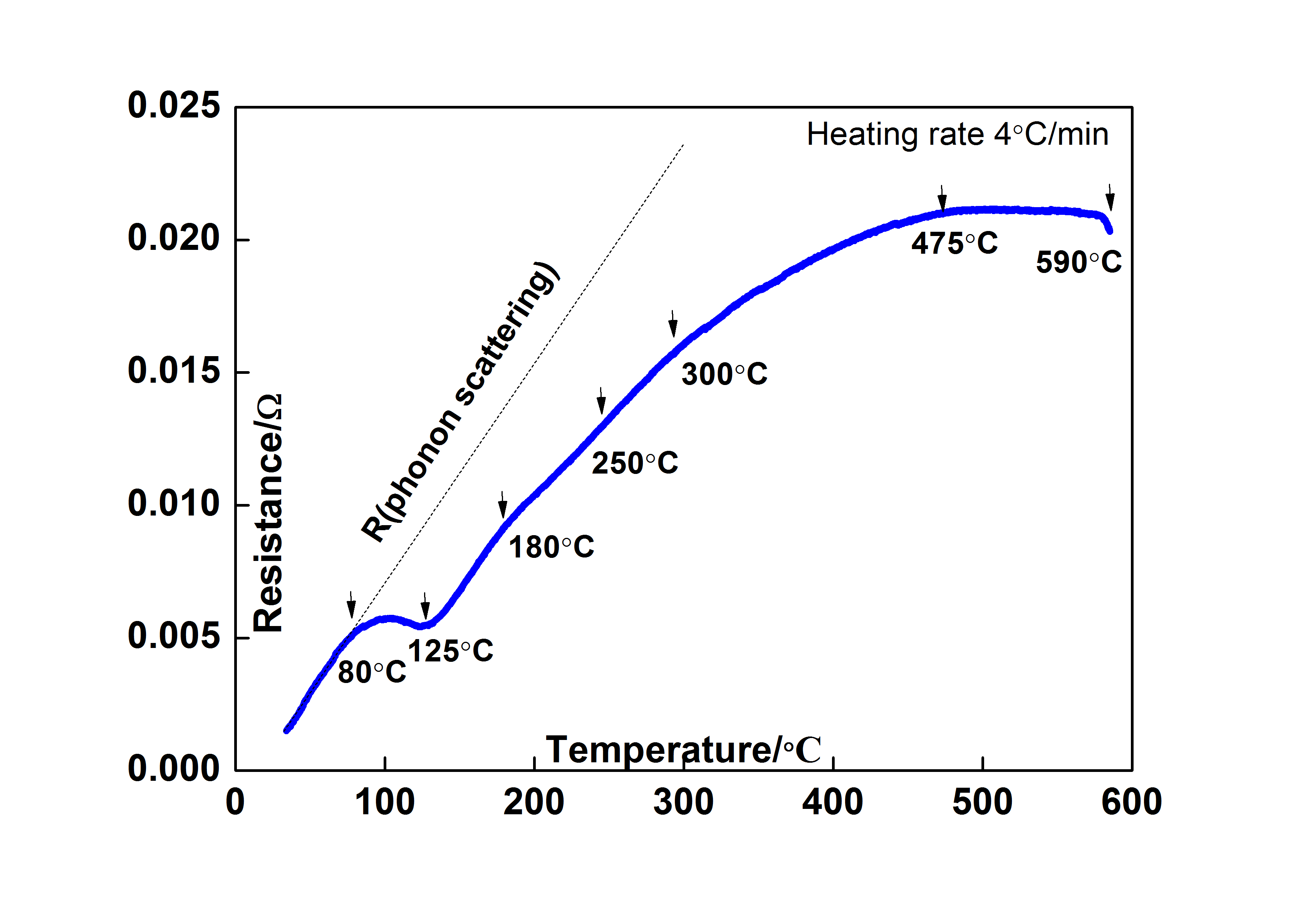
The diffusion behavior of carbon atoms of SDCM1 new hot working die steel during tempering from room temperature to 590 ℃ was studied using the resistance method, combined with the hardness measurementand microstructure analysis. The results show that during temperingat 80-125 ℃, the resistance deviation from linearlyof the experimental steel decreases, the hardness reaches peak value, this is mainly due to the diffusion of carbon atoms to dislocations, and the activation energy of the steel is 83 kJ·mol-1. During tempering at 180-250℃, the resistance deviation from linearly decreases slightly, this is mainly due to the nucleation of ε carbides. During temperingat above 300℃, the resistance increases slowlywith the increase of temperature, combined with transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis, this is mainly due to the precipitation of carbides, the precipitation difference between Fe3Ccarbide and alloy carbides can be judged by different evolution trend of resistance. When the tempering temperature increases to 590 ℃, the resistance of the experimental steel decreases sharply, this is mainly due to the large precipitation of isothermal carbides. The results show that the resistance method can clearly characterize the movement, occupation, microstructure evolution and dynamics of carbon atoms of the SDCM1 new hot working die steel during tempering, is an effective means of research.
In this work, all of tthe resistance data were measured by HTR-1 high temperature electrical resistivity measurement system which designed by Dr.zhang. The work was was published on Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2021, 42(5 ):88-95.